LC-MS data acquisition and pre-processing
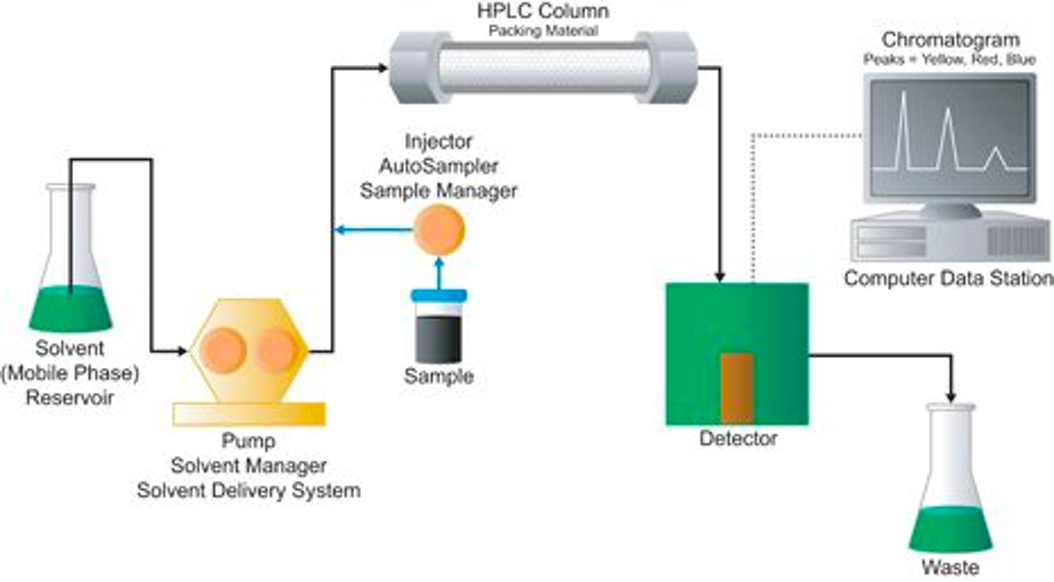
Chromatography
- The process of separating components of a mixture
- Based on an analytes’ difference in partitioning between a stationary and mobile phases

Types of liquid chromatography
- Reversed phase
- Normal phase
- HILIC (hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography)
Mass spectrometry
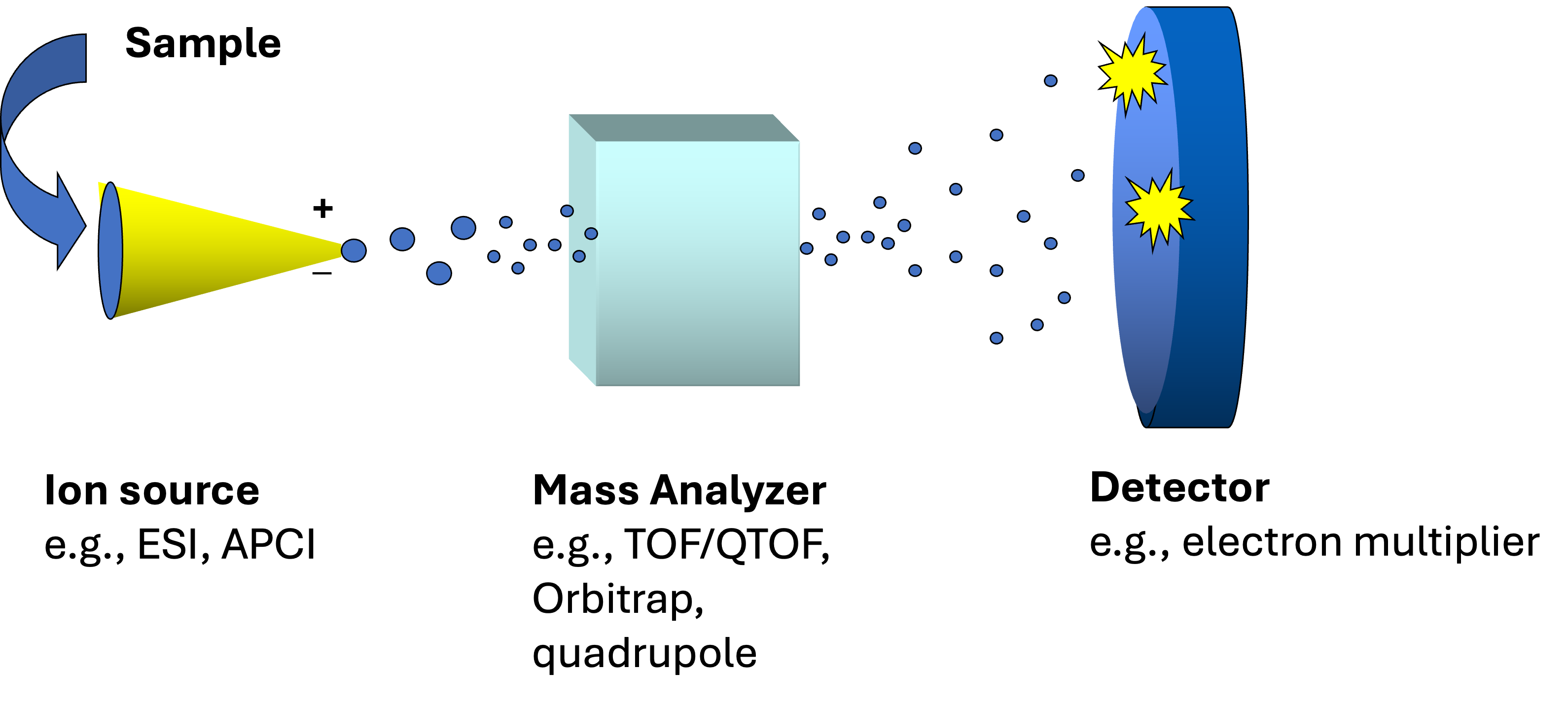
Specifics about MS
Requires gas phase ionization (no charge, no signal!)
Different ionization methods (e.g., ESI vs. APCI)
Inherently non-quantitative
- A higher signal for compound A than B doesn’t necessarily mean compound A is present in higher concentration
Ion suppression in complex mixtures
Mass analyzer: time of flight (TOF or QTOF)
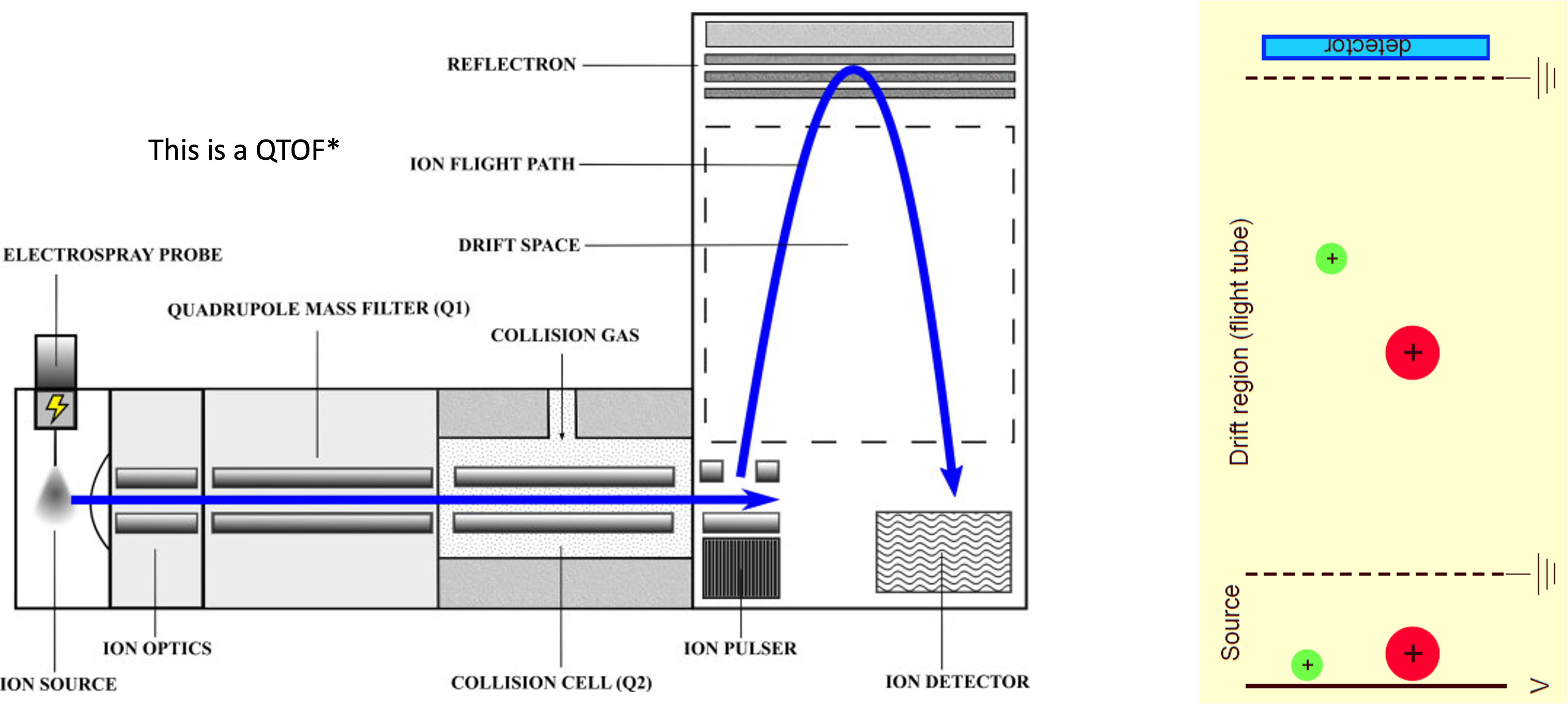 Allen and McWhinney, Clin Biochem Red 2019
Allen and McWhinney, Clin Biochem Red 2019
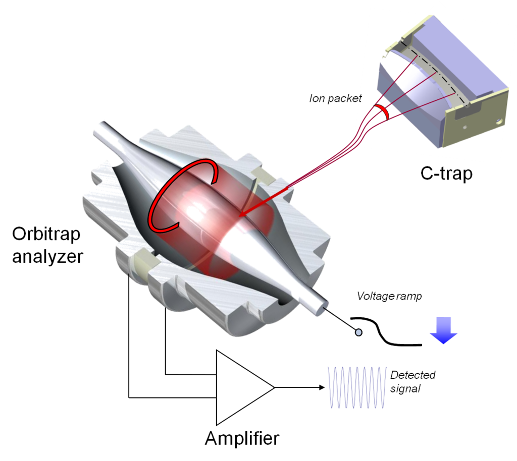
Mass analyzer: Orbitrap
MS output
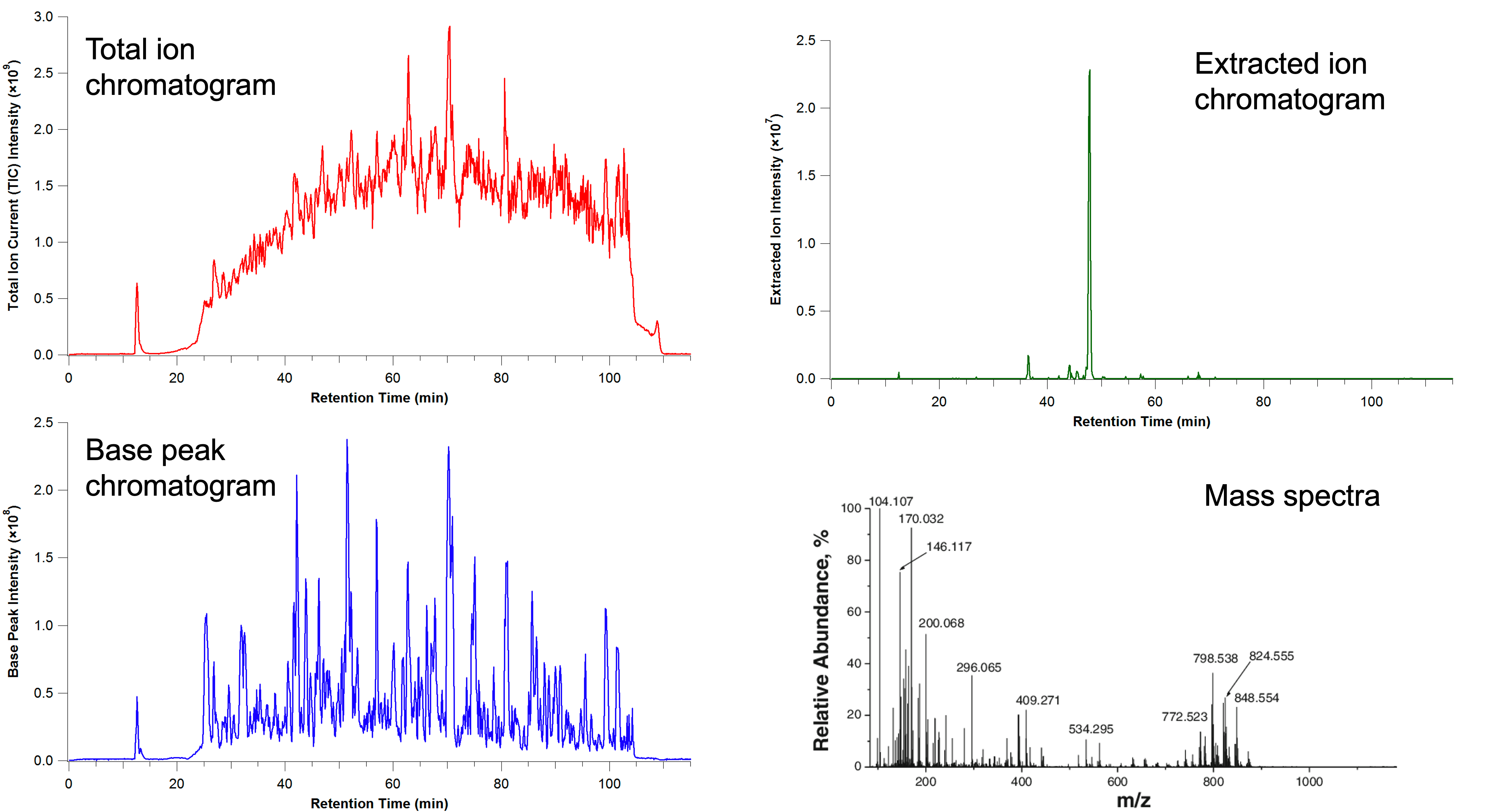
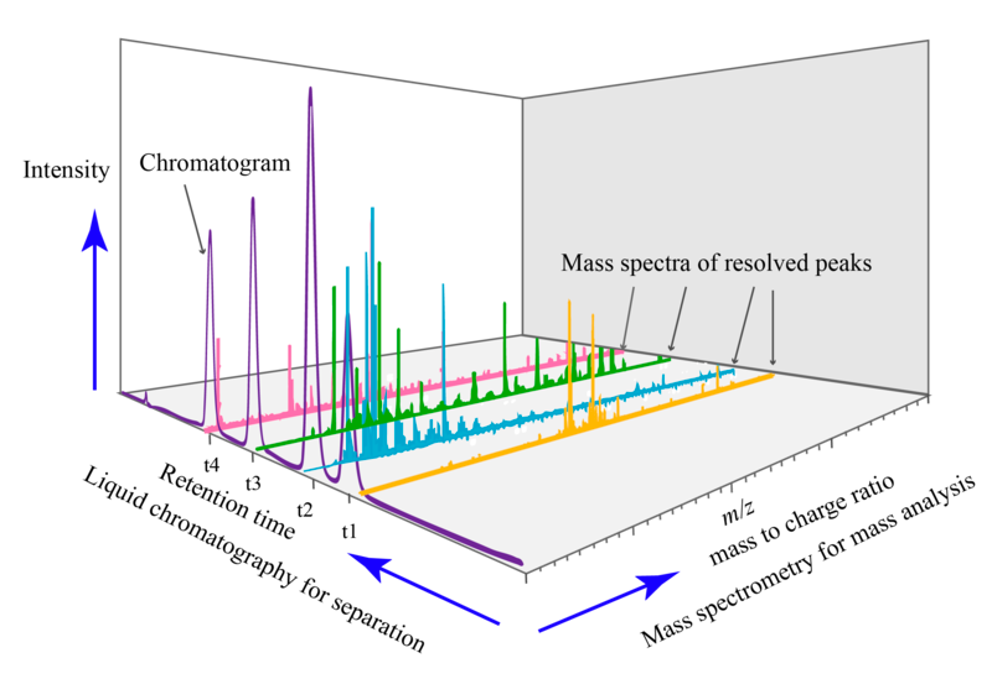
MS data is really 3D
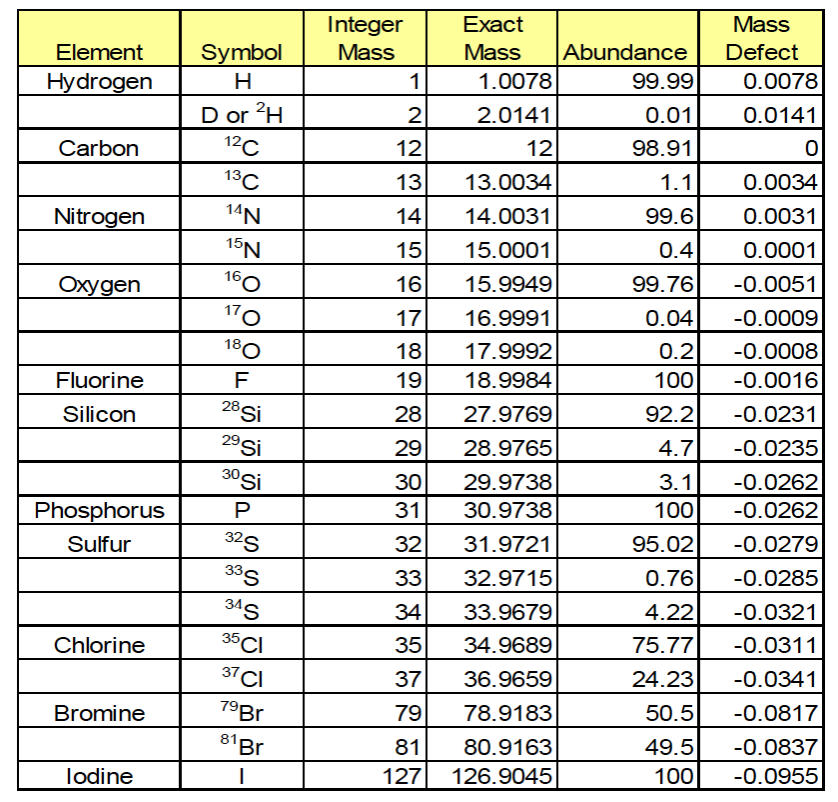
Different ways to express a mass
Nominal mass: sum of the integer masses of the constituent elements of a molecule (C=12, H=1)
Monoisotopic mass: mass of a molecular given empirical formulate calculated using the exact mass of the most abundance isotope of each element (C=12.0000, H=1.0078)
Average mass: mass of a molecule given empirical formulate calculated using the weighted average mass for each element by isotopic abundance (C=12.0112, H=1.00797)
C20H42
Nominal mass: (20 × 12) + (42 × 1) = 282
Monoisotopic mass: (20 × 12.0000) + (42 × 1.0078) = 282.3276
Average mass: (20 × 12.0112) + (42 × 1.00797) = 282.5587
Try calculating the monoisotopic mass
Tomatidine C27H45NO2

Example: Rutin
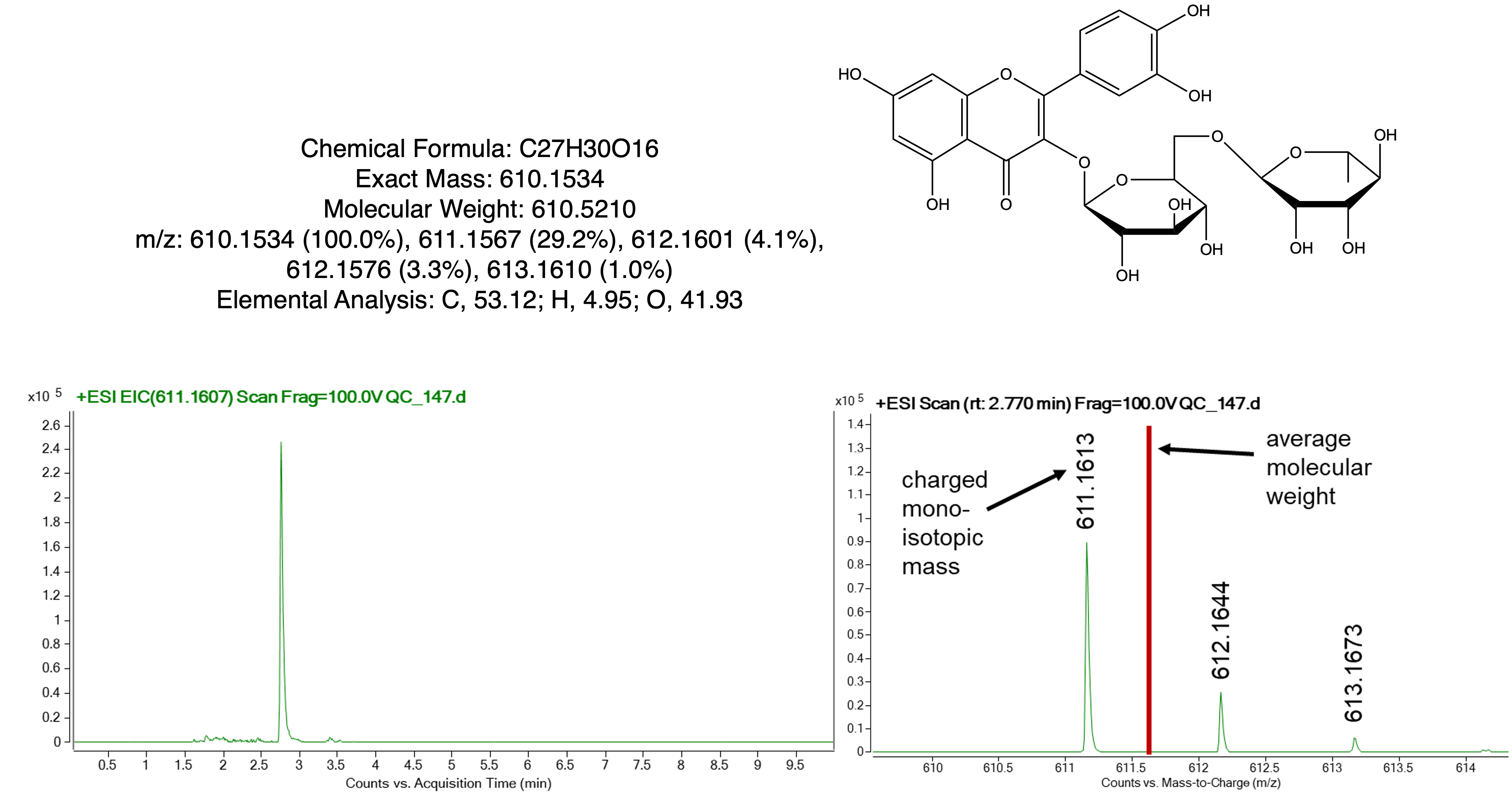
Compare experimental to exact mass in working towards a compound ID
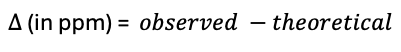
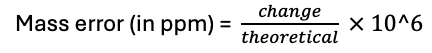
- Exact mass is calculated (theoretical)
- Accurate mass is experimental determined (observed)
Example:
- rutin observed (positive mode): 611.1613 m/z
- rutin theoretical: 610.1534
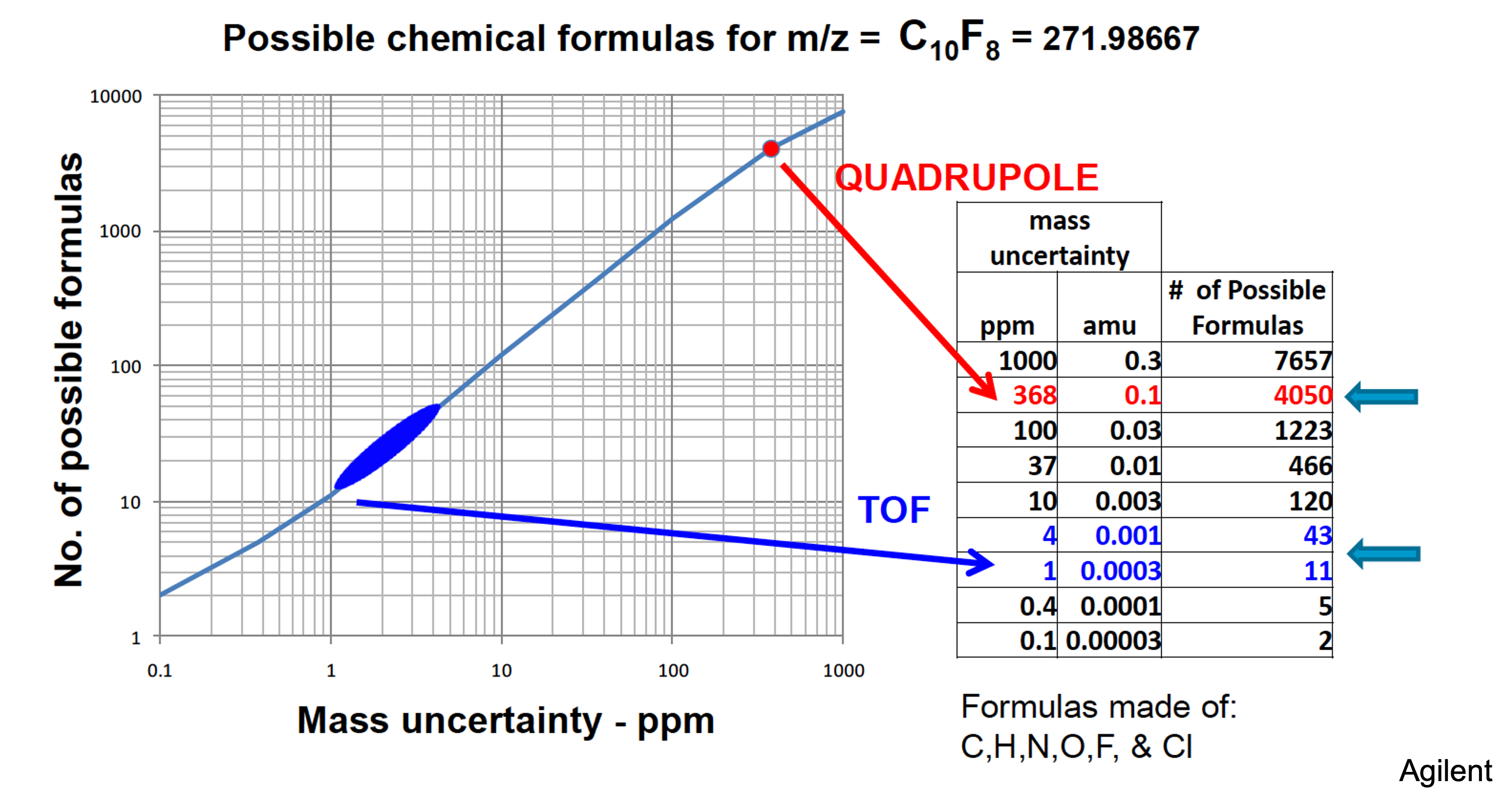
Why you need high mass accuracy for metabolomics
Standards for identity reporting
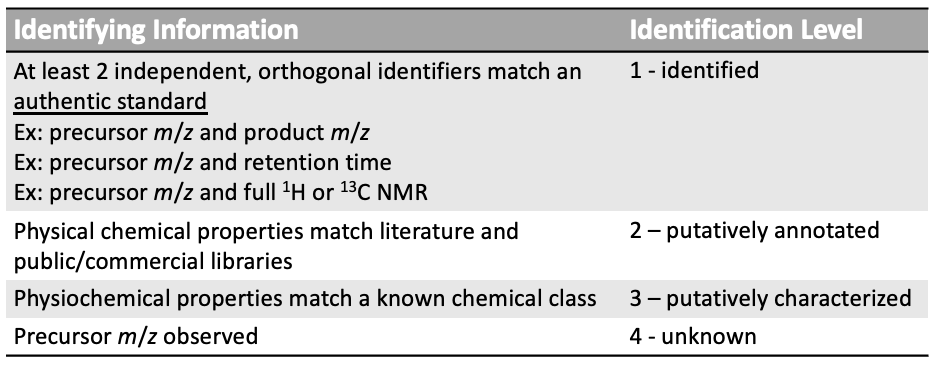
Fig. adapted from Sumner et al., Metabolomics 2007
Converting raw spectra into a feature table (i.e., pre-processing)
- Vendor software:
Agilent: Profinder
Waters: Progenesis
Thermo: Compound Discoverer
Bruker: MetaboScape
Shimadzu: LabSolutions
- Open source software:
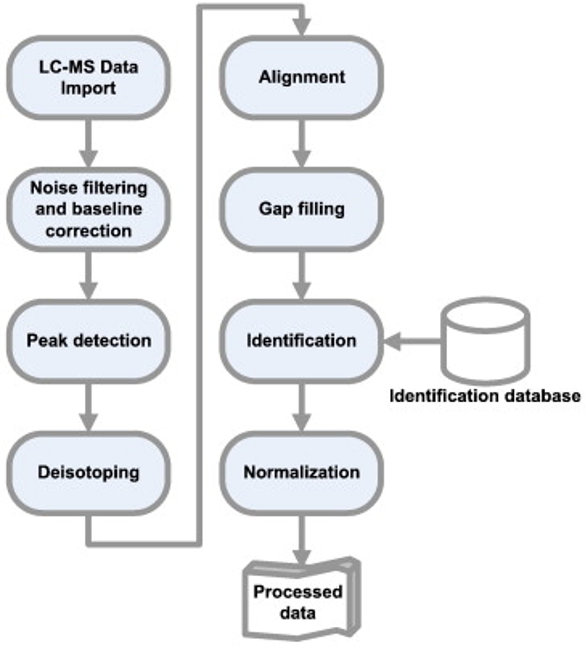
Castillo et al., Chemometrics Intelligent Lab Systems 2011
© Jessica Cooperstone, 2024